CHAPTER -13 :APPLY THE PRINCIPAL OF SEMICONDUTOR
A substance that can conduct electricity is called
the
conductor and a
substance that cannot conduct electricity is
known as the insulator. Semiconductors have properties that sit between the conductor and insulator. A diode,
integrated circuit (IC) and transistor are all made from semiconductors.
Computer chips, both for CPU and memory, are composed of semiconductor materials
A
semiconductor is a substance that has specific electrical properties that enable it to serve as a foundation for computers and other electronic devices. It is
typically a solid chemical element or
compound that conducts electricity under certain conditions but not others. This makes it an ideal medium to control
electrical current and everyday electrical appliances.
Uses of Semiconductors in
Everyday life
·
Temperature sensors are made with semiconductor devices.
·
They are used in 3D printing
machines
·
Used in microchips and self-driving cars
·
Used in calculators, solar plates, computers and other electronic devices.
TYPES OF SEMICONDUCTOR
1) Intrinsic semiconductor:
An intrinsic type of semiconductor material is made to be very pure chemically. It is made up of only a single type of element.
Germanium
(Ge) and Silicon (Si) are the most common type of intrinsic semiconductor elements. They have four valence
electrons (tetravalent). They are bound to the atom by covalent
bond at absolute zero temperature.
When the temperature rises,
due to collisions, few electrons
are unbounded and become
free to move through the lattice, thus creating an absence in its original position (hole). These free electrons and
holes contribute to the conduction of electricity
in the semiconductor. The negative and positive charge carriers are equal in number.
2) Extrinsic Semiconductor
The
conductivity of semiconductors can be greatly improved by introducing a small number of suitable replacement atoms
called IMPURITIES. The process of adding impurity
atoms to the pure semiconductor is called DOPING.
Usually, only 1 atom in 107 is replaced by a
dopant atom in the doped semiconductor.
An extrinsic semiconductor can be further classified into:
·
N-type Semiconductor
·
P-type Semiconductor
N-Type
Semiconductor
·
Mainly due to electrons
·
Entirely neutral
·
I = Ih and nh >> ne
·
Majority – Electrons and Minority – Holes
When a
pure semiconductor (Silicon or Germanium) is doped by pentavalent impurity (P, As, Sb, Bi) then, four electrons out of five valence electrons bonds with the four electrons of Ge or Si.
The fifth electron of the dopant is set free. Thus, the impurity
atom donates a free electron
for conduction in the lattice
and is called “Donar“.
Since
the number of free electron increases by the addition of an impurity, the negative charge carriers increase. Hence, it is called n-type
semiconductor.
P-Type
Semiconductor
·
Mainly due to holes
·
Entirely neutral
·
I = Ih and nh >> ne
·
Majority – Holes and Minority
– Electrons
When a pure semiconductor is doped with a trivalent impurity (B, Al, In, Ga ) then, the three valence electrons of the
impurity bonds with three of the four valence electrons
of the semiconductor.
This leaves an absence of electron (hole)
in the impurity. These impurity
atoms which are ready to accept bonded
electrons are called
“Acceptors“.
With the increase in the number of impurities, holes (the positive
charge carriers) are increased. Hence,
it is called p-type semiconductor.
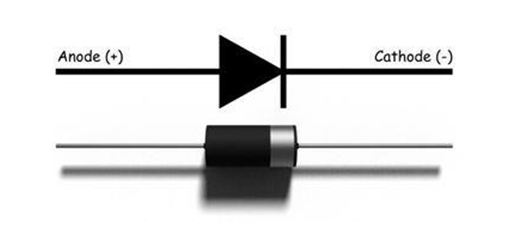
DIODE SEMICONDUTOR
A diode is a two-terminal electronic
component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance);
it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally
infinite) resistance in the other.
The diode have two points, one anode and anathoer cathode.
DIODE ARE ONE DIRECTIONAL(Positive to Negative ).
Diode are used in turning AC to DC ,
Inverters, Powe r supply etc
Working principle of semiconductor diode
N-type have a significant number of
free electrons and very few holes.
But in P-type, It has a high concentration of holes and very few free electrons. For this reason, the free electron from n side will diffuse into the p side
and recombine with holes present
there, leaving position is not movable ions in n side and creating negative immobile ions in the p-type side of the diode.
Hence, revealed positive giver
particles present in the n-type side
close to the junction edge. Correspondingly, revealed negative acceptor particles present in the p-type side close to the junction edge.
For
this reason, the number of positive ions and negative
ions will accumulate on
n-side and p side too. This region is formed
in the depletion region due to the free carrier in the region.
Because of the nearness of these
positive and negative ions, a static
electric field called as barrier potential is made over the PN junction of the diode. It is classified “barrier
potential” since it goes about
as an obstruction and opposes the further migration of gaps
and free electrons
over the junction.
.
TYPES OF DIODES
Light Emitting Diode (LED)
When an electric current between
the electrodes passes through this diode, light is produced. In other words, light is generated when a
sufficient amount of forwarding
current passes through it. In many diodes, this light generated is not visible
as there are frequency levels that do not allow visibility. LEDs are available in different colours.
There are tricolour
LEDs that can emit three colours at a time. Light colour
depends on the energy gap of the semiconductor used.
Laser Diode
It is a different type of diode as it produces coherent
light. It is highly used in CD drives,
DVDs and laser devices. These are costly when compared to LEDs and are cheaper when compared to other laser
generators. Limited life is the only drawback of these diodes.
Avalanche Diode
This diode
belongs to a reverse
bias type and operates using the avalanche effect. When voltage
drop is constant and is independent of current,
the breakdown of
avalanche takes place. They exhibit high levels of sensitivity and hence are used
for photo detection.
Zener Diode
It is the most useful type of diode as it can provide
a stable reference
voltage. These are operated
in reverse bias and break down on the arrival of a certain voltage. If current passing through the
resistor is limited, a stable voltage is generated.
Zener diodes are widely
used in power supplies to provide a reference voltage.
Zener
diodes are used for voltage regulation, as reference elements, surge suppressors, and in switching
applications and clipper
circuits
Prepared By :Mausham Aryal
(GSS 2079)